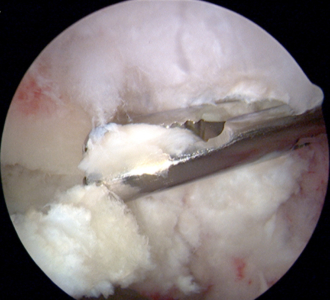
Focal cartilage damage is an area of articular hip cartilage injury caused by degenerated or damaged cartilage on what was once a normal joint surface. These areas of deteriorated cartilage can lead to pain, secondarily decreasing normal range of motion and function.
Office Appointments and Telemedicine with Dr. Carreira

You can also book an office appointment or a telemedicine visit by calling Dr. Carreira’s office at 404-355-0743. Book now.
What Are the Causes of Articular (Hip) Cartilage Injury?
There are many causes including genetics, normal wear and tear, overuse injuries, and obesity to name a few. Normal cartilage in your joints is important because this tissue cushions impacts and helps glide the movements your body makes everyday. Your doctor will evaluate you, and help make this diagnosis.
Treatment of Articular Hip Cartilage Defects
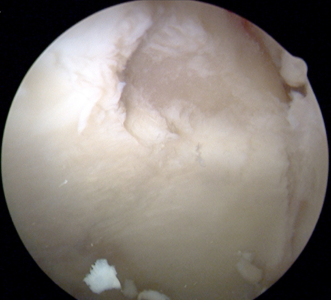
An exciting treatment option available for this condition is called an arthroscopic microfracture. This technique is performed by a highly skilled arthroscopic orthopedic surgeon and has been proven to stimulate the regeneration of hyaline-like cartilage, ultimately replacing your damaged articular cartilage with new, healthy cartilage. The technique is performed arthroscopically where 2 or 3 small portals are made (1cm in length incisions) in your skin. The damaged articular cartilage is removed, leaving behind any healthy cartilage. Then, with a special tool, small microfractures are made by poking tiny holes into the bone in the area of what was once your damaged cartilage.
Over several weeks your body regenerates new cartilaginous tissue in this area likely decreasing or eliminating pain. The technique has been shown to be effective in approximately 85% of patients and is dependent on the size of the articular cartilage injury. If there is diffuse arthritis or generalized damage of the articular cartilage, this technique is not indicated.
Hip Microfracture
In this minimally invasive hip arthroscopy procedure, the microfracture technique is demonstrated. This technique is used for articular cartilage defects, and was developed in the knee and is now used in multiple joints. The microfracture technique requires restricted weight bearing with the use of crutches or a walker for a minimum of 6 weeks after surgery and the use of continuous passive motion (CPM).
Additional videos are available for review on Dr. Carreira’s Youtube channel.
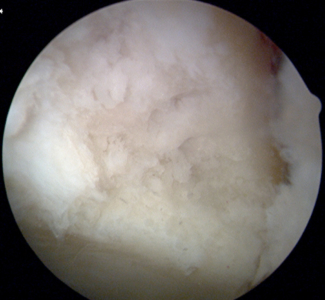
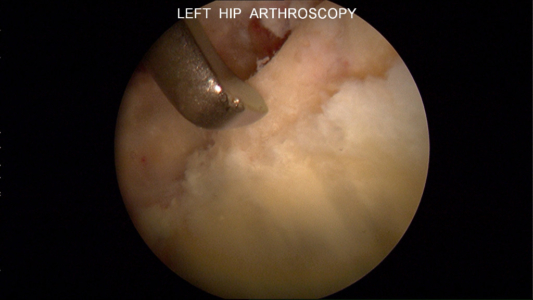
Photo of Femoral Head Chondrosis
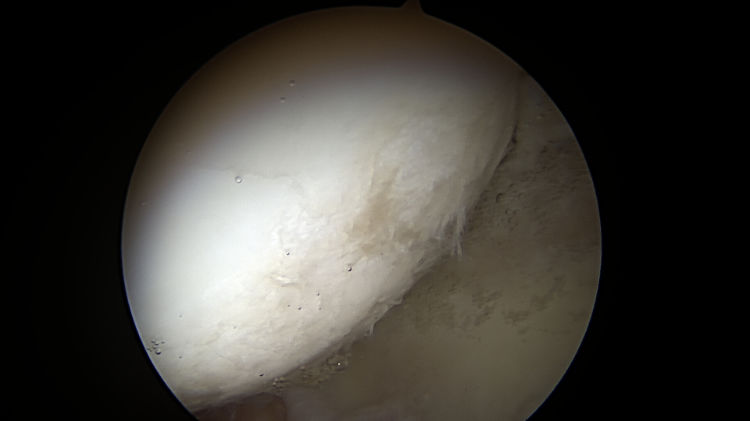
Femoral head chondrosis (cartilage damage) that is less than 50% of cartilage depth as noted during a hip arthroscopy procedure.
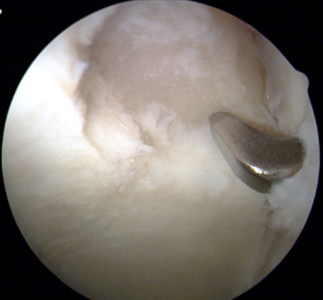
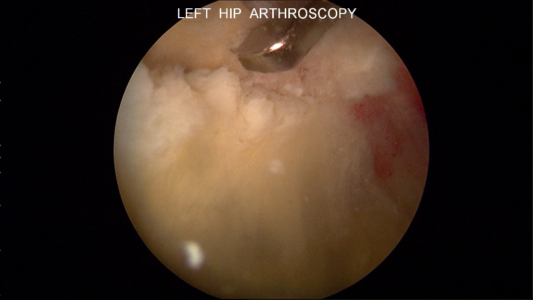
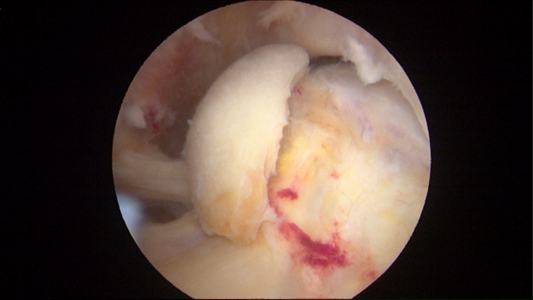
Photo of Central Osteophytes (Arthritic Boney Spurs) and more
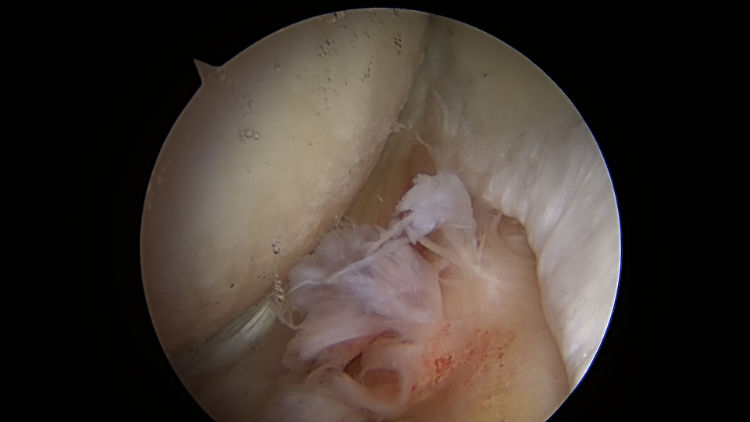
Central osteophytes (arthritic boney spurs), femoral head chondrosis (damage of the cartilage on the femoral side of the hip joint) and tear of Ligamentum teres noted during hip arthroscopy in a 47-year-old male. These findings of intra-articular damage place this patient at greater risk of needing a hip replacement in the future.